Smartphones can be a cop's best friend. They are packed with private information like emails, text messages, photos, and calling history. Unsurprisingly, law enforcement agencies now routinely seize and search phones. This occurs at traffic stops, during raids of a target's home or office, and during interrogations and stops at the U.S. border. These searches are frequently conducted without any court order.
courts the have such searches, and so as a practical matter, if the police seize your phone, there isn't much you can do after the fact to keep your data out of their hands.
However, just because the courts have permitted law enforcement agencies to search seized smartphones, doesn't mean that you—the person whose data is sitting on that device—have any obligation to make it easy for them.
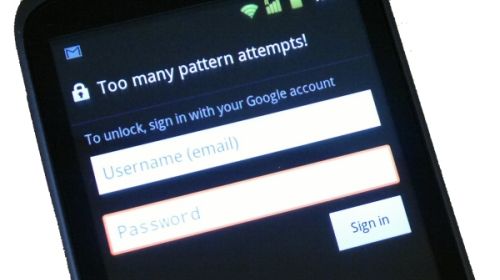
Screen unlock patterns are not your friend
The Android mobile operating system includes the capability to lock the screen of the device when it isn't being used. Android supports three unlock authentication methods: a visual pattern, a numeric PIN, and an alphanumeric password.
The pattern-based screen unlock is probably good enough to keep a sibling or inquisitive spouse out of your phone (providing they haven't seen you enter the pattern, and there isn't a smudge trail from a previous unlock that has been left behind). However, the pattern-based unlock method is by no means sufficient to stop law enforcement agencies.
After five incorrect attempts to enter the screen unlock pattern, Android will reveal a “forgot pattern?” button, which provides the user with an alternate way method of gaining access: By entering the Google account email address and password that is already associated with the device (for email and the App Market, for example). After the user has incorrectly attempted to unlock the screen unlock pattern 20 times, the device will lock itself until the user enters a correct username/password.

What this means is that if provided a valid username/password pair by Google, law enforcement agencies can gain access to an Android device that is protected with a screen unlock pattern. As I understand it, this assistance takes the form of two password changes: one to a new password that Google shares with law enforcement, followed by another that Google does not share with the police. This second password change takes place sometime after law enforcement agents have bypassed the screen unlock, which prevents the government from having ongoing access to new email messages and other Google account-protected content that would otherwise automatically sync to the device.
Anticipatory warrants
As The Wall Street Journal , Google was served with a search warrant earlier this year compelling the company to assist agents from the FBI in unlocking an Android phone seized from a pimp. According to the Journal, Google refused to comply with the warrant. The Journal did not reveal why Google refused, merely that the warrant had been filed with the court with a handwritten note by a FBI agent stating, "no property was obtained as Google Legal refused to provide the requested information."
It is my understanding, based on discussions with individuals who are familiar with Google's law enforcement procedures, that the company will provide assistance to law enforcement agencies seeking to bypass screen unlock patterns, provided that the cops get the right kind of court order. The company insists on an , which the Supreme Court as “a warrant based upon an affidavit showing probable cause that at some future time, but not presently, certain evidence of crime will be located at a specific place.”
Although a regular search warrant might be sufficient to authorize the police to search a laptop or other computer, the always-connected nature of smartphones means that they will continue to receive new email messages and other communications after they have been seized and searched by the police. It is my understanding that Google insists on an anticipatory warrant in order to cover emails or other communications that might sync during the period between when the phone is unlocked by the police and the completion of the imaging process (which is when the police copy all of the data off of the phone onto another storage medium).
Presumably, had the FBI obtained an anticipatory warrant in the case that the Wall Street Journal wrote about, the company would have assisted the government in its attempts to unlock the target's phone.
Praise for Google
The fact that Google can, in some circumstances, provide the government access to data on a locked Android phone should not be taken as evidence that Google is designing government backdoors into its software. If anything, it is a solid example of the fact that when presented with a choice between usability and security, most large companies offering services to the general public tend to lean towards usability (for example, and can provide law enforcement agencies access to users' data stored with their respective cloud storage services).
The existence of the screen unlock pattern bypass is likely there because a large number of consumers forget their screen unlock patterns. Many of those users are probably glad that Google lets them restore access to their device (and any data on it), rather than forcing them to perform a factory reset whenever they forget their password.
However, as soon as Google provides a feature to consumers to restore access to their locked devices, the company can be forced to provide law enforcement agencies access to that same functionality. As the old saying goes, “If you build it, they will come.”
In spite of the fact that Google has prioritized usability over security, Google's legal team has clearly put their customers' privacy first.
First, the company has insisted on a stricter form of court order than a plain-vanilla search warrant, and then refused to provide assistance to law enforcement agencies that seek assistance without the right kind of order.
Second, by providing the government access to the Android device via a (temporary) change to the users' Gmail password, Google has ensured that the target of the surveillance receives an automatic email notice that their password has been changed. Although the email they receive won't make it explicit that the government has been granted access to their mobile device, it will still serve as a hint to the target that something fishy has happened.
Third, by changing the user's password a second time, Google has prevented the government from having ongoing, real-time access to the surveillance target's emails. There is, I believe, no law requiring Google to take this last step—Google has done it to protect the privacy of the user, and to deny the government what would otherwise be an indefinite email wiretap not approved by the courts.
For real protection you need full-disk encryption
Of the three screen lock methods available on Android (pattern, PIN, password), Google only offers a username/password based bypass for the pattern lock. If you'd rather that the police not be able to gain access to your device this way (and are comfortable with the risk of losing your data if you are locked out of your phone), I recommend not using a pattern-based screen lock, and instead using a PIN or password.
However, it’s important to understand that while locking the screen of your device with a PIN or password is a good first step towards security, it is not sufficient to protect your data. forensic analysis tools can be used to directly copy all data off of a device and onto external media. To prevent against such forensic imaging, it is important to encrypt data stored on a device.
Since version 3.0 (Honeycomb) of the OS, Android has included support for full disk encryption, but it is not enabled by default. If you want to keep your data safe, enabling this feature is a must.
Unfortunately, Android currently uses the same PIN or password for both the screen unlock and to decrypt the disk. This design decision makes it that users will pick a short PIN or password, since they will probably have to enter their screen unlock dozens of time each day. Entering a 16-character password before making a phone call or obtaining GPS directions is too great of a usability burden to place on most users.
Using a shorter letter/number PIN or password might be good enough for a screen unlock, but disk encryption passwords must be much, much longer to be able to withstand brute force attacks. Case in point: released at the Defcon hacker conference this summer the disk encryption of Android devices that are protected with 4-6 digit numeric PINs in a matter of seconds.
Hopefully, Google's engineers will at add new functionality to Android to let you use a different PIN/password for the screen unlock and full disk encryption. In the meantime, users who have their device can download a that will allow you to choose a different (and hopefully much longer) password for disk encryption.
What about Apple?
The recent Wall Street Journal story on Google also raises important questions about the phone unlocking assistance Apple can provide to law enforcement agencies. An Apple spokesperson told the Journal that the company "won't release any personal information without a search warrant, and we never share anyone's passcode. If a court orders us to retrieve data from an iPhone, we do it ourselves. We never let anyone else unlock a customer's iPhone."
The quote from Apple's spokesperson confirms what others have hinted at for some time: that the company will unlock phones and extract data from them for the police. For example, an anonymous law enforcement source earlier this year that Apple has for at least three years helped police to bypass the lock code on iPhones seized during criminal investigations.
Unfortunately, we do not know the technical specifics of how Apple retrieves data from locked iPhones. It isn't clear if they are brute-forcing short numeric lock codes, or if there exists a backdoor in iOS that the company can use to bypass the encryption. Until more is known, the only I can offer is to disable the “Simple Passcode” feature in iOS and instead use a long, alpha-numeric passcode.

