Privacy and Surveillance
FBI v. Fikre
Whether the government can overcome the voluntary cessation exception to mootness by removing an individual from the No Fly List when the government has not repudiated its decision to place him on the List and remains free to return him to the List for the same reasons and using the same procedures he alleges were unlawful.
Status: Ongoing
View Case
Learn About Privacy and Surveillance
Featured
U.S. Supreme Court
Apr 2022

Privacy and Surveillance
+2 Issues
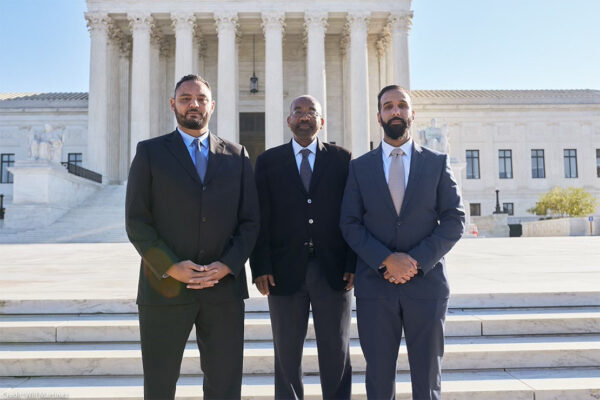
FBI v. Fazaga
In a case scheduled to be argued before the U.S. Supreme Court on November 8, 2021, three Muslim Americans are challenging the FBI’s secret spying on them and their communities based on their religion, in violation of the Constitution and federal law. In what will likely be a landmark case, the plaintiffs — Yassir Fazaga, Ali Uddin Malik, and Yasser Abdelrahim — insist that the FBI cannot escape accountability for violating their religious freedom by invoking “state secrets.” The plaintiffs are represented by the Center for Immigration Law and Policy at UCLA School of Law, the ACLU of Southern California, the American Civil Liberties Union, the Council for American Islamic Relations, and the law firm of Hadsell Stormer Renick & Dai.
All Cases
35 Privacy and Surveillance Cases
U.S. Supreme Court
Feb 2023
Privacy and Surveillance
Wikimedia v. NSA - Challenge to Upstream Surveillance
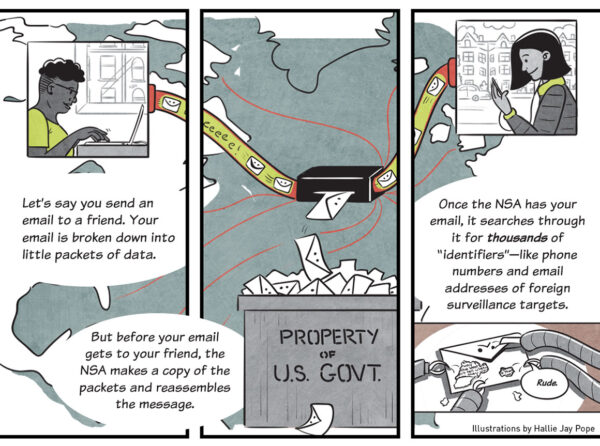
The ACLU is challenging the constitutionality of the NSA’s mass interception and searching of Americans’ international Internet communications. At issue is the NSA’s “Upstream” surveillance, through which the U.S. government systematically monitors private emails, messages, and other data flowing into and out of the country on the Internet’s central arteries. The ACLU’s lawsuit was brought on behalf of the Wikimedia Foundation and eight legal, human rights, and media organizations, which together engage in trillions of sensitive communications and have been harmed by Upstream surveillance.
Explore case
U.S. Supreme Court
Feb 2023

Privacy and Surveillance
Wikimedia v. NSA - Challenge to Upstream Surveillance
The ACLU is challenging the constitutionality of the NSA’s mass interception and searching of Americans’ international Internet communications. At issue is the NSA’s “Upstream” surveillance, through which the U.S. government systematically monitors private emails, messages, and other data flowing into and out of the country on the Internet’s central arteries. The ACLU’s lawsuit was brought on behalf of the Wikimedia Foundation and eight legal, human rights, and media organizations, which together engage in trillions of sensitive communications and have been harmed by Upstream surveillance.

Court Case
Apr 2022
Privacy and Surveillance
U.S. v. Muhtorov
The ACLU and the Office of the Federal Public Defender of Colorado jointly represented Jamshid Muhtorov in challenging the warrantless surveillance of his communications under Section 702 of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA), and the lawfulness of other spying methods the government used against him. Mr. Muhtorov was the first person ever to receive notice from the government that Section 702 had been used to spy on their communications. In a split decision in December 2021, the Tenth Circuit court of appeals ruled against Mr. Muhtorov.
Explore case
Court Case
Apr 2022

Privacy and Surveillance
U.S. v. Muhtorov
The ACLU and the Office of the Federal Public Defender of Colorado jointly represented Jamshid Muhtorov in challenging the warrantless surveillance of his communications under Section 702 of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA), and the lawfulness of other spying methods the government used against him. Mr. Muhtorov was the first person ever to receive notice from the government that Section 702 had been used to spy on their communications. In a split decision in December 2021, the Tenth Circuit court of appeals ruled against Mr. Muhtorov.

U.S. Supreme Court
Nov 2021
Privacy and Surveillance
Free Speech
ACLU v. United States
The ACLU has filed three motions in the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court (FISC) asking it to release secret opinions authorizing the surveillance of Americans. The public has a right to see the legal decisions addressing novel surveillance programs that affect our privacy and free speech rights — but many of the FISC’s opinions remained closely guarded secrets.
After the FISC and its appeals court rejected the ACLU’s public access arguments in a series of rulings, the ACLU asked the Supreme Court to review those rulings and to recognize that the public has a First Amendment right of access to the FISC’s opinions.
Explore case
U.S. Supreme Court
Nov 2021

Privacy and Surveillance
Free Speech
ACLU v. United States
The ACLU has filed three motions in the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court (FISC) asking it to release secret opinions authorizing the surveillance of Americans. The public has a right to see the legal decisions addressing novel surveillance programs that affect our privacy and free speech rights — but many of the FISC’s opinions remained closely guarded secrets.
After the FISC and its appeals court rejected the ACLU’s public access arguments in a series of rulings, the ACLU asked the Supreme Court to review those rulings and to recognize that the public has a First Amendment right of access to the FISC’s opinions.

Colorado Supreme Court
Sep 2021
Privacy and Surveillance
National Security
People v. Tafoya
This case concerns whether the government may surreptitiously record the activities around a person’s home using a remotely operated, pole-mounted video camera for an extended period of time without a warrant. On September 13, 2021, the Colorado Supreme Court held that the Fourth Amendment protects against such surveillance and requires that police obtain a warrant.
Explore case
Colorado Supreme Court
Sep 2021

Privacy and Surveillance
National Security
People v. Tafoya
This case concerns whether the government may surreptitiously record the activities around a person’s home using a remotely operated, pole-mounted video camera for an extended period of time without a warrant. On September 13, 2021, the Colorado Supreme Court held that the Fourth Amendment protects against such surveillance and requires that police obtain a warrant.

Court Case
May 2021
Privacy and Surveillance
Free Speech
Chebli v. Kable: Lawsuit Challenging Placement on No Fly List
In April 2021, the American Civil Liberties Union, the ACLU of the District of Columbia, and the ACLU of Michigan filed a lawsuit on behalf of Ahmad Chebli, whom the U.S. government wrongly placed on the No Fly List after he refused to become an FBI informant. Ten days after the ACLU filed the lawsuit, the government finally removed Mr. Chebli from the No Fly List. Because he is no longer on the No Fly List, Mr. Chebli withdrew the lawsuit, saying “I’m relieved to be off the No Fly List, but still reeling from the government’s abusive use of the list against me and its violations of my constitutional rights. I was placed on the list after I refused to become an FBI informant despite frightening and intimidating threats against me and my family. For over two years, I sought a fair process to clear my name, and the government failed to provide me with one. As a Muslim in this country, it can be easy to feel like a second-class citizen and be afraid to stand up for your rights because of the way our own government treats us. But now I feel vindicated and want my story to encourage others to stand up for their rights, because when we do, good things can happen.”
Explore case
Court Case
May 2021

Privacy and Surveillance
Free Speech
Chebli v. Kable: Lawsuit Challenging Placement on No Fly List
In April 2021, the American Civil Liberties Union, the ACLU of the District of Columbia, and the ACLU of Michigan filed a lawsuit on behalf of Ahmad Chebli, whom the U.S. government wrongly placed on the No Fly List after he refused to become an FBI informant. Ten days after the ACLU filed the lawsuit, the government finally removed Mr. Chebli from the No Fly List. Because he is no longer on the No Fly List, Mr. Chebli withdrew the lawsuit, saying “I’m relieved to be off the No Fly List, but still reeling from the government’s abusive use of the list against me and its violations of my constitutional rights. I was placed on the list after I refused to become an FBI informant despite frightening and intimidating threats against me and my family. For over two years, I sought a fair process to clear my name, and the government failed to provide me with one. As a Muslim in this country, it can be easy to feel like a second-class citizen and be afraid to stand up for your rights because of the way our own government treats us. But now I feel vindicated and want my story to encourage others to stand up for their rights, because when we do, good things can happen.”
